by Tsinghua University Press

In recent years, additive manufacturing technology has attracted considerable attention from various stakeholders. Among the different techniques, Arc wire-based direct energy deposition (DED) has experienced a notable increase in development, offering compelling advantages such as cost-effectiveness and high forming efficiency.
However, a high deposition rate results in extremely high heat input and temperature inhomogeneity, leading to a deterioration in surface quality, a reduction in material properties, an increase in residual stresses and even distortion and cracking. Consequently, the current research agenda is focused on developing methods to ensure the quality of components produced at high deposition rates.
Furthermore, additional research is necessary to gain a comprehensive understanding of Arc wire-based direct energy deposition technology, particularly regarding microstructure control and mechanical property optimization, to meet the demands of higher-performance applications.
A team led by the Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics in China conducted a literature review to identify the factors that influence the microstructure evolution of materials during the deposition process. The team employed the principle of dynamic recrystallization to investigate the influence of heat input during the deposition process and to delineate methods for controlling heat input and its operating mechanisms.
Furthermore, the article presents a comprehensive analysis of the impact of diverse process parameters on the melt pool behavior and microstructure during the deposition process, with a particular focus on the influence of process methods and deposition materials.
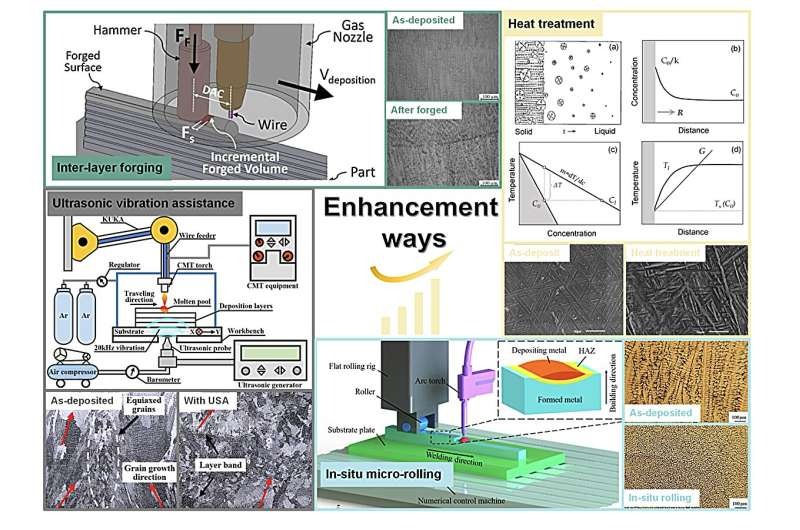
To enhance the material’s microstructure and properties, various supplementary techniques and treatments, including interlayer forging and ultrasonic impact, are examined to optimize the material’s characteristics. The effect of these methods on the microstructure and mechanical properties during deposition, as well as their respective advantages and disadvantages, are discussed in detail. This work presents novel approaches for improving the properties of materials deposited by Arc wire-based DED, thereby contributing to the advancement of the field.
The team published their work in the Journal of Advances Mechanical Science and Technology on October 15, 2024.

“In this report, we discuss the factors that influence the evolution of the material’s microstructure during the deposition process. It summarizes methods to control the heat input during deposition and highlights various heat treatment techniques to reduce defects and improve the microstructure and properties of the deposited parts. These techniques include pre-deposition, process, and post-deposition treatments.
“The study also investigates methods for introducing deformation strengthening and briefly reviews their advantages and disadvantages. Lastly, the manuscript presents the future development direction and research focus of Arc wire-based DED,” said Dr. Qian, an associate professor at the Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics (NUAA).
This manuscript provides valuable insights for researchers in related fields. It enables them to comprehensively understand methods to enhance the microstructure and properties of Arc wire-based DED parts in a short timeframe. Additionally, it offers insights into the functional mechanisms that can be applied in their research work, thereby expanding the potential applications of Arc wire-based DED parts.
Nevertheless, research into the solidification characteristics of different materials and the deposition characteristics of different processes continues to yield increasingly detailed insights and innovative methods for regulating the microstructure and mechanical properties of Arc wire-based directed energy deposition parts.
These research directions on microstructure and mechanical property control should focus on the following four aspects, as previously highlighted by Dr. Qian. The research directions on microstructure and mechanical property control should focus on the following four aspects: control of heat input, control of solidification behavior, control of the dynamic recrystallization process, and control of deleterious phases and defects.
Other participants in the research include Jingjing Shi, Professor Honghua Su, Professor Wenfeng Ding, Professor Yucan Fu of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, and Shihao Sun of Jiangsu JITRI Institute of Precision Manufacturing.
More information: Jingjing SHI et al, Enhancement of material microstructure and properties in Arc wire-based direct energy deposition: A short review, Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Science and Technology (2024). DOI: 10.51393/j.jamst.2024015